Scripts
Automate your workflow with pre-request and post-request scripts using JavaScript.
Overview
Scripts let you run JavaScript code before a request is sent (pre-request) or after a response is received (post-request). Use them to set variables, modify requests dynamically, validate responses, or chain requests together.
Echolon provides a scripting API giving you access to environment variables, request data, and response data through global objects.
JSON, Date, Math, btoa, atob, and more.
Pre-request Scripts
Pre-request scripts run before your request is sent. They're perfect for:
- Generating timestamps or random values
- Computing authentication signatures
- Setting dynamic headers or body content
- Reading and setting environment variables
Example: Adding a timestamp header
// Add a timestamp to every request
req.setHeader('X-Request-Time', Date.now().toString());
console.log('Request will be sent at:', new Date().toISOString());Post-request Scripts
Post-request scripts run after the response is received. Use them to:
- Validate status codes and response bodies
- Extract values (like tokens) to use in subsequent requests
- Log response data for debugging
- Store values in environment variables
Example: Extracting and storing a token
// Parse response and store auth token
const data = JSON.parse(res.body);
if (data.token) {
echo.setEnvVar('auth_token', data.token);
console.log('Token saved to environment');
}
console.log('Response status:', res.status);Scripting API
Echolon provides three global objects in scripts: echo, req, and res.
echo Object
The echo object provides methods to interact with environment and runtime variables.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
echo.getEnvVar(name) | Get an environment variable value |
echo.setEnvVar(name, value) | Set an environment variable (persists for the session) |
echo.getVar(name) | Get a runtime variable (request-scoped) |
echo.setVar(name, value) | Set a runtime variable (request-scoped) |
echo.sleep(ms) | Pause execution for specified milliseconds |
Example:
// Get base URL from environment
const baseUrl = echo.getEnvVar('baseUrl');
console.log('Using base URL:', baseUrl);
// Set a variable for later use
echo.setEnvVar('lastRequestTime', Date.now().toString());req Object
The req object provides access to the current request. In pre-request scripts,
you can both read and modify the request.
| Property/Method | Description |
|---|---|
req.url | The request URL (read/write) |
req.method | The HTTP method (read/write) |
req.headers | Headers object (read/write) |
req.body | Request body (read/write) |
req.getUrl() | Get the request URL |
req.setUrl(url) | Set the request URL |
req.getMethod() | Get the HTTP method |
req.setMethod(method) | Set the HTTP method |
req.getHeaders() | Get all headers as an object |
req.getHeader(name) | Get a specific header value (case-insensitive) |
req.setHeaders(headers) | Replace all headers |
req.setHeader(name, value) | Set a specific header |
req.getBody() | Get the request body |
req.setBody(body) | Set the request body |
Example:
// Log current request details
console.log('Making', req.method, 'request to', req.url);
// Add authentication header
const token = echo.getEnvVar('auth_token');
if (token) {
req.setHeader('Authorization', 'Bearer ' + token);
}
// Modify the request body
const body = JSON.parse(req.getBody() || '{}');
body.timestamp = Date.now();
req.setBody(JSON.stringify(body));res Object
The res object is available only in post-request scripts and provides
read-only access to the response.
| Property/Method | Description |
|---|---|
res.status | HTTP status code (e.g., 200, 404) |
res.statusText | HTTP status text (e.g., "OK", "Not Found") |
res.headers | Response headers object |
res.body | Response body as string |
res.responseTime | Request duration in milliseconds |
res.getStatus() | Get the status code |
res.getStatusText() | Get the status text |
res.getHeaders() | Get all headers as an object |
res.getHeader(name) | Get a specific header (case-insensitive) |
res.getBody() | Get the response body |
res.getResponseTime() | Get the response time in ms |
Example:
// Check response status
if (res.status !== 200) {
console.error('Request failed with status:', res.status, res.statusText);
}
// Parse JSON response
try {
const data = JSON.parse(res.body);
console.log('Response data:', data);
// Store user ID for next request
if (data.id) {
echo.setEnvVar('userId', data.id.toString());
}
} catch (e) {
console.error('Failed to parse response as JSON');
}
// Log performance
console.log('Request completed in', res.responseTime, 'ms');Sample Scripts
Echolon includes built-in sample scripts to help you get started. Access them from the dropdown menu in the Scripts tab.
Pre-request Script Examples
Set Environment Variable
// Set an environment variable
echo.setEnvVar('my_env_variable', 'my_env_value');
console.log('Environment variable set: my_env_variable');Add Authentication Header
// Add Bearer token authentication
const token = echo.getEnvVar('auth_token');
if (token) {
req.setHeader('Authorization', 'Bearer ' + token);
console.log('Added auth header');
} else {
console.warn('No auth token found in environment');
}Generate Timestamp
// Add timestamp to request
const timestamp = Date.now();
req.setHeader('X-Timestamp', timestamp.toString());
console.log('Timestamp:', new Date(timestamp).toISOString());Generate UUID
// Generate a simple UUID v4
const uuid = 'xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx'.replace(/[xy]/g, (c) => {
const r = Math.random() * 16 | 0;
const v = c === 'x' ? r : (r & 0x3 | 0x8);
return v.toString(16);
});
echo.setVar('requestId', uuid);
req.setHeader('X-Request-ID', uuid);
console.log('Generated UUID:', uuid);Post-request Script Examples
Log Response
// Log response details
console.log('Status:', res.status, res.statusText);
console.log('Response time:', res.responseTime, 'ms');
console.log('Body preview:', res.body.substring(0, 200));Extract Token
// Extract and store auth token from response
try {
const data = JSON.parse(res.body);
if (data.token || data.access_token) {
const token = data.token || data.access_token;
echo.setEnvVar('auth_token', token);
console.log('Token extracted and saved');
}
} catch (e) {
console.error('Could not parse response:', e.message);
}Validate Response
// Validate response status and content
if (res.status >= 400) {
console.error('Request failed:', res.status, res.statusText);
} else {
console.log('Request successful');
// Check content type
const contentType = res.getHeader('content-type');
if (contentType && contentType.includes('application/json')) {
const data = JSON.parse(res.body);
console.log('Response contains', Object.keys(data).length, 'fields');
}
}Viewing Script Output
After sending a request, script output (console logs, errors) appears in the Scripts tab in the response panel. This tab shows:
- Pre-request output: Logs from the pre-request script
- Post-request output: Logs from the post-request script
- Execution time: How long each script took to run
- Errors: Any script errors with stack traces
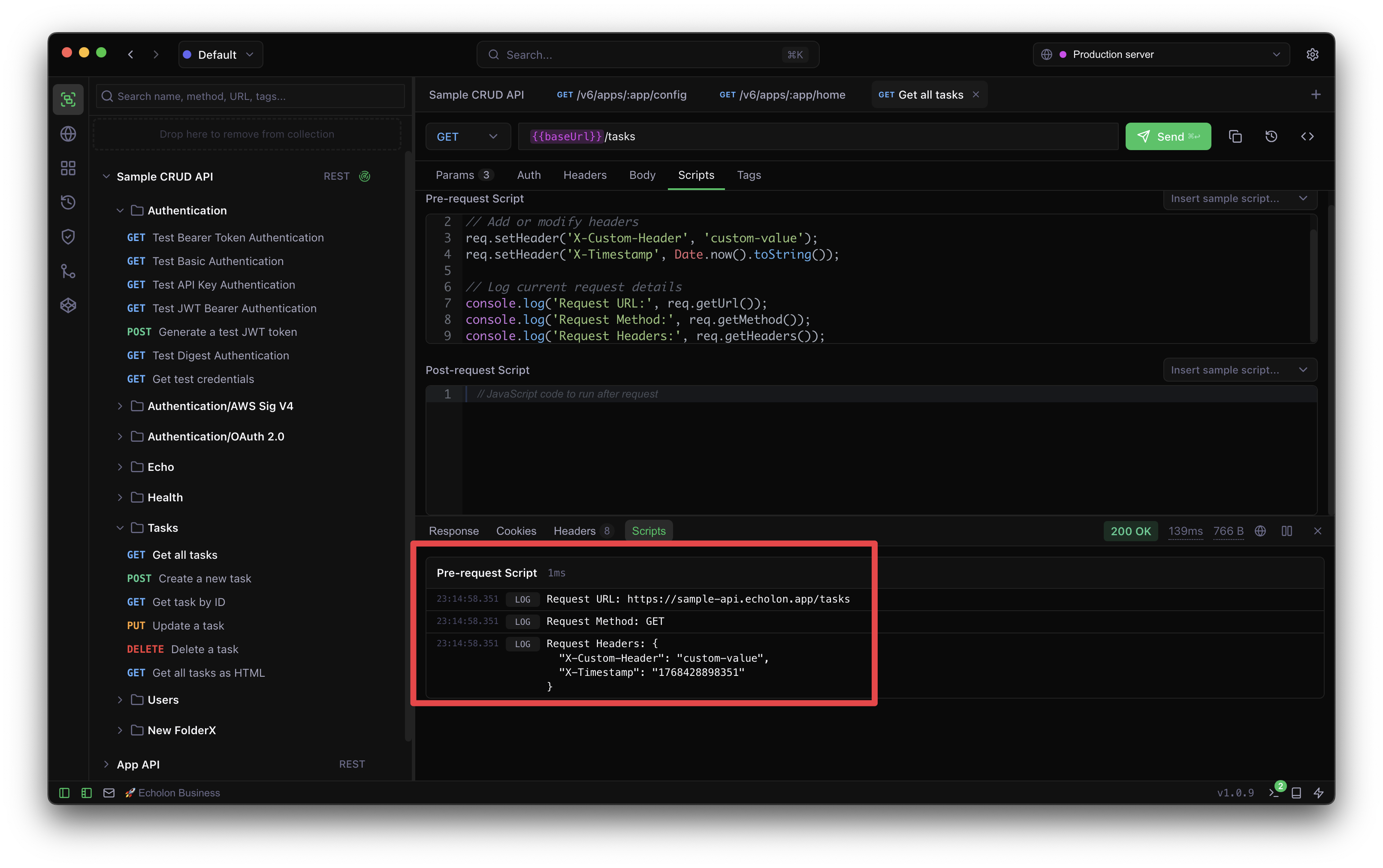
console.log(), console.warn(),
console.error(), and console.info() to output debug information.
All console output is captured and displayed in the Scripts tab.
Available Globals
In addition to echo, req, and res, scripts have access to:
console— log, warn, error, info methodsJSON— parse and stringifyDate— date manipulationMath— mathematical operationsbtoa/atob— Base64 encoding/decodingencodeURIComponent/decodeURIComponentparseInt,parseFloat,isNaN,isFiniteArray,Object,String,Number,Boolean